International Data Corporation (IDC) is a global provider of market intelligence and advisory services for information technology, telecommunications, and consumer technology. IDC’s analysis and insight helps IT professionals, business executives, and the investment community make fact-based technology decisions.
This particular IDC study highlights the critical role of the record-to-report (R2R) process in ensuring accurate financial reporting and compliance, emphasizing its importance for CFOs, investors, and shareholders. It identifies key areas for improvement and the desire among CFOs for end-to-end solutions that reduce reliance on ERP systems. The document evaluates various vendors based on their capabilities to support the R2R process, offering insights to help technology buyers make informed decisions.
Embrace the future of finance with end-to-end R2R solutions, transforming CFOs’ strategic agility and competitive advantage. Record to report is the foundation of finance, and the holistic process needs to be looked at for improvement to insights and data for a company.
The record-to-report (R2R) process is a fundamental aspect of the financial reporting cycle; it is crucial for CFOs, investors, and shareholders as they provide a detailed and accurate account of a company’s financial activities. For CFOs, these records are the foundation for all financial reporting and analysis, enabling them to monitor cash flows, manage budgets, and ensure regulatory compliance. Investors and shareholders rely on accounting records to assess the financial health and performance of the company, making informed decisions about buying, holding, or selling their shares. Transparent and accurate accounting records build trust, reduce the risk of fraud, and enhance the credibility of financial statements, ultimately supporting better investment decisions and fostering a stable and trustworthy business environment.
In IDC’s 2023 Office of the CFO Survey, we asked what the top process improvement areas for record to report were. Revenue recognition/revenue accounting management, transfer pricing/intercompany transactions, and financial reporting analytics were the top 3 process improvements that financial leaders felt needed improvement. In another smaller survey we conducted in 2023 with only 31 CFOs, we asked what they wished technology vendors would do: one, they wanted them to stop overselling capabilities and second, they wanted technology vendors to provide an end-to-end solution for all finance capabilities that will enable you not to need an enterprise resource planning (ERP) system. For this reason, we have focused on the end-to-end solution for record to report to provide the full capabilities for the entire process. It’s worth noting that many of these accounting technology vendors do not perform the “record” or book of record capability but rather integrate with an ERP system to record the transactions and be the book of record. While there are a few ERP vendors included in this document, it’s to allow a full scope comparison of some of the ERP vendors in their capabilities to fill the needs of the full end-to-end record-to-report process.
Record to report ensures the accuracy and integrity of financial data. This process encompasses the collection, processing, and consolidation of financial information, transforming raw data into comprehensive financial statements. Accurate financial reporting is essential for compliance with regulatory requirements and for building trust with stakeholders. A CFO relies on the R2R process to ensure that the financial statements reflect the true financial position and performance of the organization, minimizing the risk of errors or fraudulent activities.
In addition, the R2R process provides the CFO with valuable insights for strategic decision-making. Through detailed and timely financial reports, the CFO can analyze key financial metrics, identify trends, and assess the financial health of the company. This information is critical for making informed decisions regarding budgeting, forecasting, and resource allocation. The ability to access reliable financial data quickly enables the CFO to respond proactively to market changes, optimize financial performance, and drive the organization toward its strategic goals. Effective R2R processes, therefore, directly contribute to the strategic agility and competitive advantage of the organization.
Last, the R2R process supports effective communication with external stakeholders. Investors, creditors, regulatory bodies, and other stakeholders rely on accurate and timely financial reports to make informed decisions about their engagement with the company. For a CFO, maintaining transparent and reliable financial reporting through the R2R process is crucial for building and sustaining trust and confidence among these stakeholders. This transparency can lead to better credit ratings, more favorable loan terms, and increased investor confidence, all of which are vital for the financial stability and growth of the organization. Thus the R2R process not only ensures compliance and operational efficiency but also enhances the company’s reputation and relationships with key external parties.
Why Will the CFO and Controller Focus on Record to Report?
One of the top KPIs and metrics that the CFO and controllers look at is the cycle time for the record-to-report process and its crucial role in maintaining efficient financial operations. Leading companies typically complete the consolidation cycle within two days after the general ledger closes, which is vital for timely financial reporting and strategic decision-making, enabling quick responses to market conditions and stakeholder needs. We have seen goals of five-to-seven day close from start to finish of the record-to-report cycle time in metrics at enterprise companies. The overall cycle time for R2R can vary based on organizational complexity, system efficiency, and the level of automation. Companies that utilize advanced technologies, such as cloud-enabled solutions and automated financial systems, significantly reduce their cycle times, enhancing the accuracy and reliability of their financial reports. Best-in-class R2R processes focus on minimizing manual interventions and ensuring high data integrity, which not only shortens cycle time but also reduces errors and rework. A few of the most manual processes that exist in the record-to-report process are revenue accounting, transfer pricing, intra-/intercompany transactions, and reporting analytics/insights that slow down the close process; hence they made it to the top process improvement list in IDC’s 2023 Office of the CFO Survey. As businesses strive for greater efficiency, the trend toward shorter and more efficient R2R cycles is expected to continue, driven by technological advancements and the increasing demand for real-time financial insights. One other reason that the CFO and controllers will focus on the record-to-report processes is the number of resources and overtime the closing cycle often takes, creating burnout and blackout days for vacation and time off, limiting flexibility for accountants. The talent pipeline is smaller than in the past, and finance professionals including accountants will be seeking more flexible positions that limit or eliminate the need for overtime.
Compliance Is at the Core of Record to Report
Global compliance issues are critical considerations for the record-to-report process due to the increasingly complex regulatory environment. Record to report is where many regulators look for records to prove compliance. While Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX) compliance (in the United States) and anti–money laundering (AML) and financial crime prevention have been major drivers over the past decade for financial professionals, there have been a few recent areas of concern that have been in the compliance area like environmental, social, and governance (ESG) standards; transfer pricing; and e-invoicing for tax compliance.
The cost of implementing and maintaining Sarbanes-Oxley compliance for U.S. companies can be substantial, varying significantly based on company size, complexity, and the number of controls in place. For example, companies with more than 12 locations spend an average of $1.561 million per year on compliance compared with $657,383 for those with fewer locations. Despite these high costs, many companies are finding that investing in automation and advanced compliance tools can help streamline processes and reduce long-term expenses. These tools include intelligent audit management, workflow automation, and continuous monitoring, which not only help in managing compliance costs but also enhance the effectiveness of internal controls.
Anti–money laundering and financial crime prevention will always be top priorities for R2R compliance. Regulatory agencies worldwide are intensifying their scrutiny and enforcement actions in this area, resulting in significant fines for noncompliance. In the United Kingdom alone, financial institutions have faced fines totaling £476 million for AML violations. Companies must implement robust AML controls and continuously monitor transactions to mitigate risks and ensure compliance with international standards.
As different countries implement their own ESG regulations, companies operating across multiple jurisdictions face the challenge of adhering to a diverse set of rules. This complexity requires rigorous data collection and reporting mechanisms to ensure compliance and avoid substantial penalties. For example, the heightened focus on ESG regulations means that companies must invest significantly in compliance activities to meet these diverse requirements, as failure to comply can result in substantial fines and damage to reputation. Some have turned to green or sustainability accounting to solve the demonstrating ESG compliance due to EU’s Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD). We did not include green accounting in this IDC MarketScape, but it’s something to keep in mind if your company is large and potentially moving into the EU market.
While AI can enhance efficiency in detecting suspicious activities and managing risks, it introduces complexities in ensuring ethical use and regulatory compliance. There are a few AI methods that are rules based and are easier to audit. Similarly, the evolving regulation of digital assets requires companies to stay updated with new laws and adapt their reporting processes accordingly. The integration of AI into accounting and compliance brings several concerns, including data privacy and security, as AI systems often handle sensitive financial information that must be protected against breaches. There is also the issue of bias and fairness, as AI algorithms can reflect biases present in their training data, leading to discriminatory outcomes. Transparency and explainability are critical, particularly in compliance, where understanding the decision-making process is essential. Ensuring AI systems adhere to regulatory requirements is challenging due to the dynamic nature of both technology and regulations. The accuracy and reliability of AI outputs is paramount, as errors in financial reporting can have serious consequences. In addition, the potential for job displacement among accounting professionals, ethical considerations, and the high cost and complexity of implementing AI solutions must be considered. Ongoing maintenance and updates are necessary to keep AI systems effective and compliant, and organizations must also address legal liability issues arising from AI use. Addressing these concerns requires robust data governance, continuous monitoring, and a commitment to ethical AI practices.
IDC MARKETSCAPE VENDOR INCLUSION CRITERIA
A critical point in this research effort is to meet the following inclusion criteria:
- Vendors will be included based on them meeting IDC’s functionality requirements for R2R:
▪ The vendor must have a cloud-enabled solution.
▪ One-third of the customers must be global customers.
▪ There must have been a solution offered in the past two years.
▪ The solution must be suitable for enterprise-sized companies. - Vendor inclusion will also be based on the capability to provide at least three of the following capabilities:
▪ Accounting record financial transactions
▪ Account reconciliation
▪ Accounting/financial consolidation
▪ Accounting close
▪ Accounting financial reporting
▪ SEC filing
▪ Intercompany transactions
▪ Project accounting/government accounting
▪ Accounting and financial compliance (accounting standards, audit, and
tax)
ADVICE FOR TECHNOLOGY BUYERS
When evaluating record-to-report software, it is crucial to assess the solution’s ability to integrate seamlessly with your existing financial systems and processes. Look for software that offers robust general ledger functionality, automated financial close processes, and comprehensive reconciliation features. Ensure that the software can handle multicurrency and multi-GAAP requirements if your organization operates globally. In addition, prioritize solutions that offer real time data processing and reporting capabilities to enhance the accuracy and timeliness of financial information. This will help you make informed decisions and comply with regulatory requirements more efficiently. When considering R2R solutions, think about the company strategy such as future M&A activities global presence, and global future expansions. These items can add complexities that many companies sometimes forget, or companies may see online reviews from existing customers that do not have these current complexities and think these offerings might be a good fit for them.
Another important aspect to consider is the software’s user-friendliness and the quality of support and training resources. The software should have an intuitive interface that facilitates ease of use for your financial team. Comprehensive training materials and responsive customer support are essential to ensure smooth implementation and ongoing usage. In addition, evaluate the software’s scalability to accommodate future growth and changing business needs. Security features, such as data encryption and access controls, are also critical to protect sensitive financial information. By carefully considering these factors, along with the potential complexities of your company’s strategic activities, you can choose an R2R solution that enhances your financial reporting processes and supports your organization’s long-term objectives.
VENDOR SUMMARY PROFILES
This section briefly explains IDC’s key observations resulting in a vendor’s position in the IDC MarketScape. While every vendor is evaluated against each of the criteria outlined in the Appendix, the description here provides a summary of each vendor’s strengths and challenges.
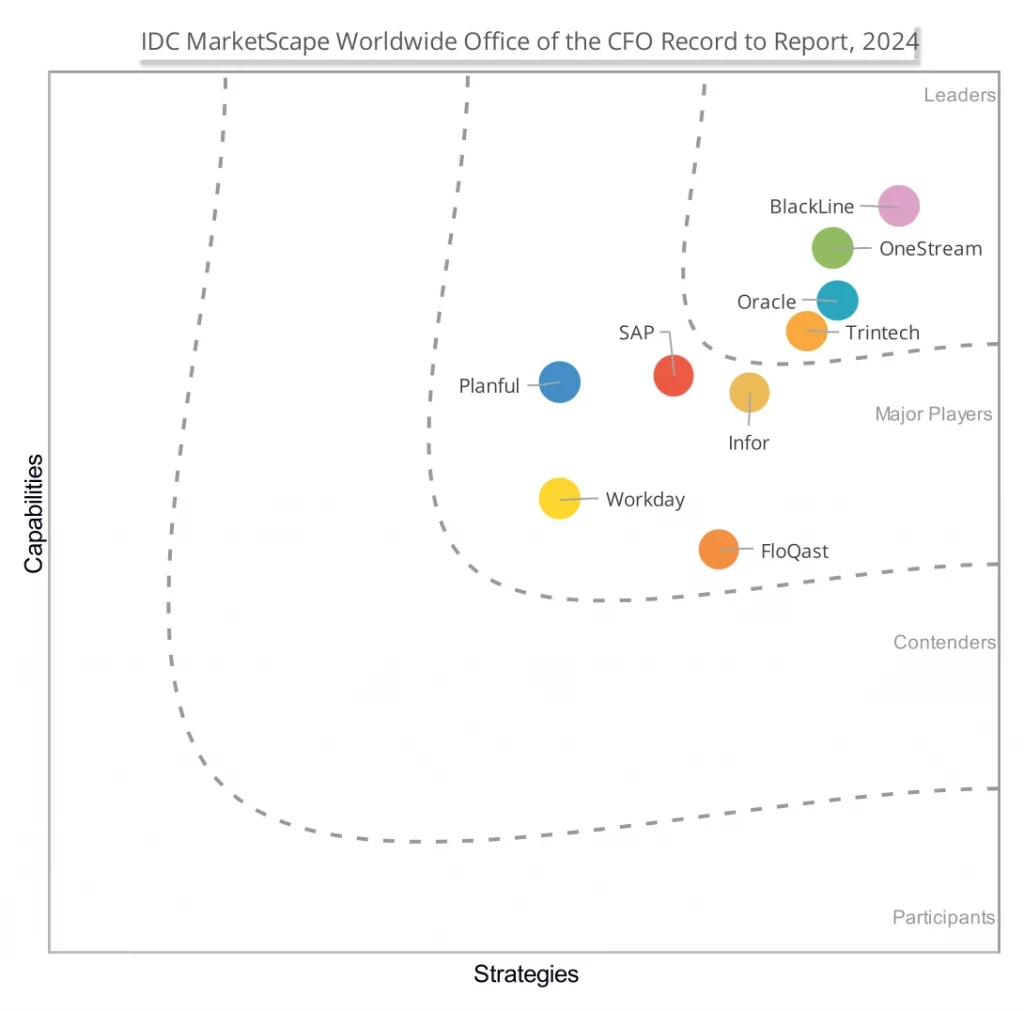
OneStream
After a thorough evaluation of OneStream’s strategies and capabilities, IDC has positioned the company in the Leaders category within this 2024 IDC MarketScape for office of the CFO record to report.
OneStream Software, founded in 2012 and headquartered in Birmingham, Michigan, specializes in corporate performance management (CPM) solutions, with a strong focus on accounting and financial management. OneStream offers a unified, cloud-based platform designed to streamline financial processes such as close, consolidation, reporting, planning, and analysis. The platform’s technical capabilities for accounting include real-time data integration, advanced financial consolidation, and detailed reporting functionalities. It also supports automated workflows and compliance management, enhancing accuracy and efficiency in financial operations. OneStream’s solution is highly configurable, allowing organizations to tailor it to their specific accounting needs and extend its functionality through the OneStream Solution Exchange, thereby improving financial decision-making and operational agility.
OneStream Strengths
- Dashboard and financial reporting capabilities: OneStream offers comprehensive and customizable dashboards for financial reporting and insights. In addition, the platform is integrated and connected to Microsoft Power BI to enhance reporting and insights across the business.
- Solution Exchange (add-on capabilities): OneStream offers a mostly free marketplace of solutions to add functionality to your record-to-report processes, so if there is something unique because of your industry or business process, you might be able to leverage a prebuilt application add on to help with a pain point or efficiency.
- Road map: OneStream has a robust AI road map. One specific area that is in beta testing includes “Sensible Gen AI,” which will “provide a purpose built chatbot” that will bring financial insights combined with other business context to your financial data to help users with financial analysis and operational insights.
OneStream Challenges
- SEC filings: OneStream uses partners for the SEC filings capability. This can often add additional cost to perform the full end-to-end process in the United States.
- Intercompany: While OneStream can perform the accounting eliminations piece, it relies on other sources and solutions for the up-front transactional parts of the process such as agreement/pricing. The validation or checking of the T&Cs between the entities might slow down the closing process.
When to Consider OneStream
Consider OneStream if you want a comprehensive record-to-report solution with additional financial functionality like forecasting, planning, and performance reporting.
APPENDIX – Reading an IDC MarketScape Graph
For the purposes of this analysis, IDC divided potential key measures for success into two primary categories: capabilities and strategies.
Positioning on the y-axis reflects the vendor’s current capabilities and menu of services and how well aligned the vendor is to customer needs. The capabilities category focuses on the capabilities of the company and product today, here and now. Under this category, IDC analysts will look at how well a vendor is building/delivering capabilities that enable it to execute its chosen strategy in the market.
Positioning on the x-axis, or strategies axis, indicates how well the vendor’s future strategy aligns with what customers will require in three to five years. The strategies category focuses on high-level decisions and underlying assumptions about offerings, customer segments, and business and go-to-market plans for the next three to five years.
The size of the individual vendor markers in the IDC MarketScape represents the market share of each individual vendor within the specific market segment being assessed.
IDC MarketScape Methodology
IDC MarketScape criteria selection, weightings, and vendor scores represent well researched IDC judgment about the market and specific vendors. IDC analysts tailor the range of standard characteristics by which vendors are measured through structured discussions, surveys, and interviews with market leaders, participants, and end users. Market weightings are based on user interviews, buyer surveys, and the input of IDC experts in each market. IDC analysts base individual vendor scores, and ultimately vendor positions on the IDC MarketScape, on detailed surveys and interviews with the vendors, publicly available information, and end-user experiences in an effort to provide an accurate and consistent assessment of each vendor’s characteristics, behavior, and capability.
Market Definition
Record to report (R2R) is a financial process used by organizations to gather, process, and deliver relevant, timely, and accurate information to stakeholders. It encompasses the entire cycle of financial and operational data collection, processing, and reporting. Here is a breakdown of the key components and stages of the R2R process:
- Data collection: This initial step involves collecting financial data from various sources, including transactions, journal entries, and operational data. It is crucial to ensure that the data is accurate and complete for reliable reporting.
- Recording transactions: Financial transactions are systematically recorded in the appropriate ledgers, often using double-entry accounting. This step ensures that all financial activities are documented and categorized correctly.
- Reconciliation: This involves comparing different sets of data to ensure consistency and accuracy across accounts. Reconciliation helps in identifying and rectifying discrepancies in financial records, such as differences between bank statements and company ledgers.
- Consolidation: For organizations with multiple subsidiaries or departments, consolidation involves combining financial data from various sources to create a unified set of financial statements. This process ensures that the financial information reflects the company’s overall performance.
- Reporting: The consolidated financial data is then used to generate reports, such as income statements, balance sheets, cash flow statements, and other financial and management reports. These reports are crucial for internal decision-making and for fulfilling external reporting requirements to stakeholders like investors, regulators, and tax authorities.
- Analysis and review: The final stage involves analyzing the financial reports to derive insights into the organization’s financial health and operational efficiency. It also includes reviewing the reports for accuracy
and compliance with accounting standards and regulatory requirements.
The R2R process is fundamental to the financial management of an organization, providing essential information that supports strategic planning, operational decision-making, and compliance with regulatory requirements. It requires a robust framework of accounting principles, internal controls, and financial management practices to ensure the integrity and reliability of reported financial information.